Twitter #VAPP5932; Presenter: Scott Salyer (VMware)
This session was focused on the various Microsoft SQL server high availability options and how they mesh with vSphere and its HA options. Unlike Exchange 2013, SQL 2012 has several HA architectures to choose from. Some applications may only support one or two SQL HA models, so don’t jump on a particular bandwagon without doing a requirements analysis and product compatibility research. For example, only recently have applications started to support SQL 2012 AlwaysOn AGs, and even then, they may not support them using SSL encryption. Also, don’t just build a SQL cluster for the hell of it. Carefully consider your requirements, since clustering is somewhat complex. Do you really need 99.999% availability? Do you have the skillset to manage it?
Finally, some DBAs may be stuck in a rut and think that physical SQL clusters are better than virtualizing them. With today’s hypervisors and best practices, there’s no reason why tier-1 SQL databases can’t be fully virtualized. However, that requires careful planning, sizing, and following best practices. Don’t think that SQL will run inherently slower on vSphere, because it’s not vSphere that maybe impacting performance. It’s one or more subsystems that were not properly configured or tuned which is making it run slow. As we move towards the fully SDDC (software defined datacenter) virtualizing all workloads is important to realizing all of the benefits of moving away from physical instances of services.
Agenda
- Why virtualize
- Causes of downtime and planning
- Baseline HA
- AlwayOn AGs
- SQL Server failover cluster
- Rolling Upgrades
- DR and Backup
Causes of Downtime
- Planned downtime – Software upgrade, HW/BIOS upgrades
- Unplanned downtime – Datacenter failure, server failure, I/O failure, software data corruption, user error
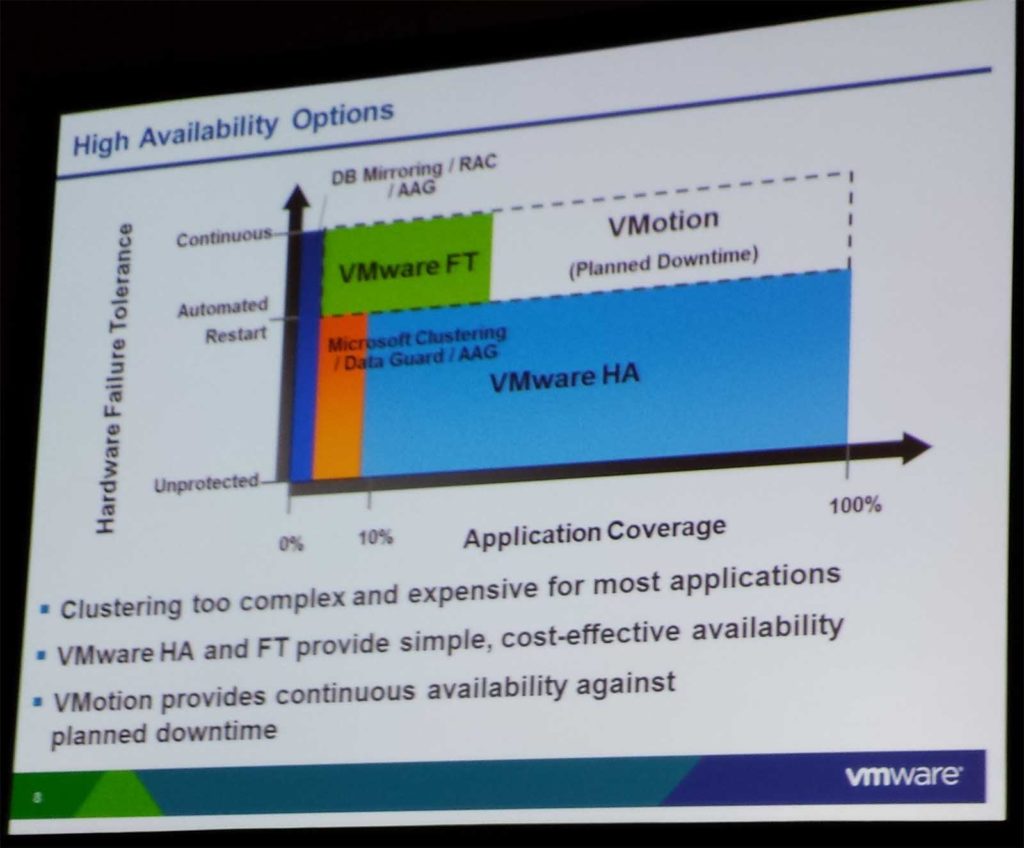
Native Availability Features
- Failover Clustering – Local redundancy, instance failover, zero data loss. Requires RDMs; can’t use VMDKs. Not the current preferred option.
- Database mirroring – Local server and storage redundancy, DR, DB failover, zero data loss with high safety mode
- Log Shipping – Multiple DR sites, manual failover required, app/user error recovery
- AlwaysOn – New in 2012, multiple secondary copies
- DB mirroring, log shipping and AlwaysOn are fully supported by HA, DRS
Planning a Strategy
- Requirements – RTO and RPOs
- Evaluating a technology
- What’s the cost for implementing and expertise?
- What’s the downtime potential?
- What’s the data loss exposure?
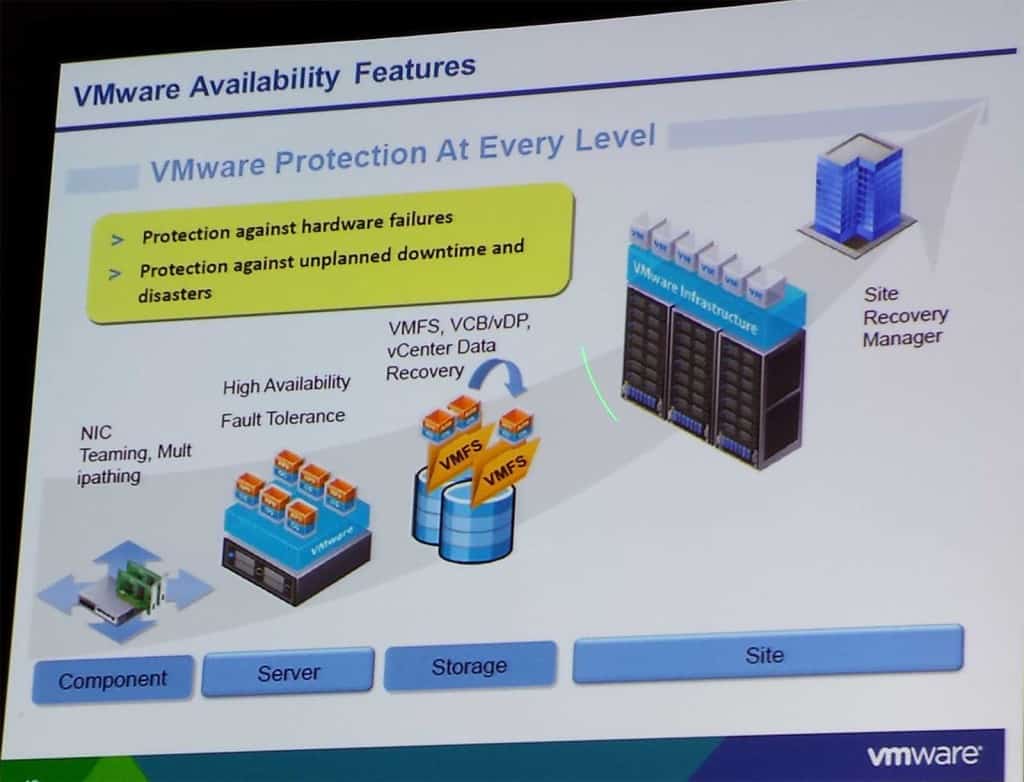
VMware Availability Features
- HA protections against host or OS system failure
- What is your SLA for hardware failures? Re-host your cluster on VMware for faster node recovery
- VM Mobility (DRS) – Valid for all SQL HA options except failover clustering
- Storage vMotion
AlwaysOn High Availability
- No shared storage required
- Database replication over IP
- Leverage ALL vSphere HA features, including DRS and HA
- Readable secondary
- Compatible with SRM
- Protects against HW, SW and DB corruption
- Compatible with FC, iSCSi, NFS, FCoE
- RTO in a few seconds
Deploying AlwaysOn
- Ensure disks are thick eagered zeroed disks
- Create DRS anti-affinity to avoid running VMs on the same host
- Create Windows Failover cluster – use node and file share majority
- Create AG for database
- Create database listener for the AG
- Monitor AG on the SQL dashboard
SQL Server Failover Clustering
- Provides application high-availability through a shared disk architecture
- Must use RDMs and FC or iSCSI
- No protection from database corruption
- Good for legacy app support that are not mirror aware
- DRS and vMotion are not available
- KB article 1037959 for support matrix
Rolling Upgrades
- Build up a standby SQL server, patch, then move DBs to standby server and change VM name/IP to production name
- Think about using vCenter orchestrator for automating the rolling patch upgrade process
Disaster Recovery and Backup
- VMware vCenter SRM
- Use AlwaysOn to provide local recovery
- Use SRM to replicate to a recovery site
- Backup – In guest backup can increase CPU utilization